前言
jaeger 是一个比较常用的分布式追踪服务,后端可以选 es、cassandra 等存储,我司线上就是用了 es 作为 jaeger 存储。
jaeger 用 es 做查询后端的时候有个坏毛病:它会自动按日期分割日志 span,一天一个 index。直接结果就是一段时间没管线上的 jaeger,过一段时间就会发现 jaege 里啥也查不出来了。翻 jaeger 的日志就会看到下面的内容:
{
"level": "error",
"ts": 1649751249.9240348,
"caller": "config/config.go:141",
"msg": "Elasticsearch part of bulk request failed",
"map-key": "index",
"response": {
"_index": "jaeger-span-2022-04-12",
"_type": "_doc",
"status": 400,
"error": {
"type": "illegal_argument_exception",
"reason": "Validation Failed: 1: this action would add [10] total shards, but this cluster currently has [2998]/[3000] maximum shards open;"
}
},
"stacktrace": "github.com/jaegertracing/jaeger/pkg/es/config.(*Configuration).NewClient.func2\n\tgithub.com/jaegertracing/jaeger/pkg/es/config/config.go:141\ngithub.com/olivere/elastic.(*bulkWorker).commit\n\tgithub.com/olivere/elastic@v6.2.35+incompatible/bulk_processor.go:588\ngithub.com/olivere/elastic.(*bulkWorker).work\n\tgithub.com/olivere/elastic@v6.2.35+incompatible/bulk_processor.go:501"
}
此时检查 GET /_cat/shards 或 GET /_cat/allocation 都能看到分片数量达到了日志里记录的 2998 个。
原因
jaeger产生大量分片
elasticsearch 官方文档指出,每个 index 会被切分成1或多个分片(shards),每个分片都可能在节点间复制,以防硬件故障。
Each index in Elasticsearch is divided into one or more shards, each of which may be replicated across multiple nodes to protect against hardware failures.
而据我观察(sorry,没有文档),jaeger 每天创建的 index 都包含至少 5 个 primary 分片,一个 replica 分片。可以通过请求index/_settings这个api端点来检查索引会分配的分片和冗余数量。
HTTP/1.1 200 OK
content-encoding: gzip
content-length: 239
content-type: application/json; charset=UTF-8
{
"jaeger-span-2022-04-12": {
"settings": {
"index": {
"creation_date": "1649749148182",
"mapping": {
"nested_fields": {
"limit": "50"
}
},
"number_of_replicas": "1",
"number_of_shards": "5",
"provided_name": "jaeger-span-2022-04-12",
"requests": {
"cache": {
"enable": "true"
}
},
"uuid": "s2i5GZtpTzm3Kp4fIldwrQ",
"version": {
"created": "7090199"
}
}
}
}
}
而检查 GET /_cat/indices 可以发现,jaeger 创建的 index 包括 jaeger-service-yyyy-mm-dd 和 jaeger-span-yyyy-mm-dd 两种,很容易算出预期每月可能产生 336~372 个新的分片。
es每个节点分片数量受限
关于节点分片数量限制,官方文档的说法是这样的:
index.routing.allocation.total_shards_per_nodeThe maximum number of shards (replicas and primaries) that will be allocated to a single node. Defaults to unbounded.
...
cluster.routing.allocation.total_shards_per_node(Dynamic) Maximum number of primary and replica shards allocated to each node. Defaults to
-1(unlimited)....
也就是默认不限制,但显然我们遇到的情况不是这样,要是 shards 数量不限制的话就根本没现在的问题了。
所以在东翻西找了一轮之后,我发现还有另一个设置项。这个设置项用 shards per node limits 当关键词搜索的时候没找到,在 GET /_cluster/settings?include_defaults 里翻出来了:max_shards_per_node。
然后我在文档里搜了下,发现官方文档其实已经做了SEO,我要是直接把错误信息贴进谷歌搜的话说不定早发现这个配置项了...
this action would add [x] total shards, but this cluster currently has [y]/[z] maximum shards open;
The
cluster.max_shards_per_nodecluster setting limits the maximum number of open shards for a cluster. This error indicates an action would exceed this limit.
max_shards_per_node的文档也很怪:
cluster.max_shards_per_node(Dynamic) Limits the total number of primary and replica shards for the cluster. Elasticsearch calculates the limit as follows:
cluster.max_shards_per_node * number of non-frozen data nodesShards for closed indices do not count toward this limit. Defaults to
1000. A cluster with no data nodes is unlimited.
虽然字面上看就是一个节点可以assign的分片数量,但实际算的是 total number of primary and replica shards for cluster。可以简单算一下,单节点集群显然只有一个 non-frozen data node,所以集群的分片上限就是 1000 * 1。线上的 3 节点集群没有 frozen data node,所以全集群最多有 1000*3 个分片。
好了问题来了,max_shards_per_node 和 total_shards_per_node 有啥区别?
total_shards_per_node 限制的是 一个节点能分配多少分片,max_shards_per_node 是 计算全集群能分配多少分片 。
例如一个三节点集群里,total_shards_per_node 是 100,但 max_shards_per_node 是 1000,可以创建出超过100个分片,但超出的分片不会被分配(没有实验过,我猜是不会 assign)。
反过来说 total_shards_per_node 比 max_shards_per_node 大的时候,虽然节点还能分配更多分片,但集群分片数已经到上限了,就会出现 this action would add [x] total shards, but this cluster currently has [y]/[z] maximum shards open; 错误了。
处理
总的来说,既然是集群内的 max_shards_per_node 配置小了,解决方法就很多:
- 把
max_shards_per_node调大,比如10000,直接10倍。 - 加 es 服务节点。
- 删旧的 jaeger 索引。
改配置显然是有点离谱的想法,等于是看到蟑螂在脚下,你选择铺张地毯,眼不见心不烦。
加节点只适合不差钱的公司,而且这么选多少是有点看公司人傻钱多的意思。
删除旧索引就正常很多,算是经典操作。更早些年应该还有个人站长写 crontab 自动删 /var/log 日志的,删旧索引本质差不多就是这个意思。
而清理旧索引也有很多做法。
jaeger-es-rollover
初始化
注意,我无法确定是否对未启用--es.use-aliases时创建的索引有效。
注意,rollover init 也会创建索引和分片,如果你已经碰到了上面的问题,直接 rollover init 会失败,必须先手动清理。
如果只想看如何清理旧索引,请跳到 删除 部分,还不行就跳到 curator 小节。
search indices 一节所述,可以使用 jaeger-es-rollover 解决以 es 作为后端存储时的 jaeger 日志轮转问题。我要吐槽下,原文:
参考 jaeger 部署文档中 shards and replicas for elasticsearch indices 一节所述,可以使用 jaeger-es-rollover 解决以 es 作为后端存储时的 jaeger 日志轮转问题。我要吐槽下,原文:
Shards and replicas are some configuration values to take special attention to, because this is decided upon index creation. This article goes into more information about choosing how many shards should be chosen for optimization.
没有任何未配置 es 日志轮转可能产生的问题的警告。我怎么知道take special attention to是指性能会在特定条件下拉胯,还是直接把 es 服务的 shards 占满,直接搞得 es 没法服务?This article 这个链接更离谱了,半句没提为什么后面有个 elasticsearch rollover 小结。
好闲话少叙。我这里是 kubernetes 平台,docker-compose 用户或者真机部署的自己看着改。
kubectl create job --image jaegertracing/jaeger-es-rollover:latest jaeger-es-rollover-init -- /go/bin/es-rollover init http://elasticsearch-es-http.elasticsearch.svc.cluster.local:9200 --es.username=***censored*** --es.password=***censored***
换成 docker 命令就是
docker run -it --rm --net=host jaegertracing/jaeger-es-rollover:latest init http://localhost:9200 --es.username=***censored*** --es.password=***censored***
这一步会创建几个新的 index 和别名
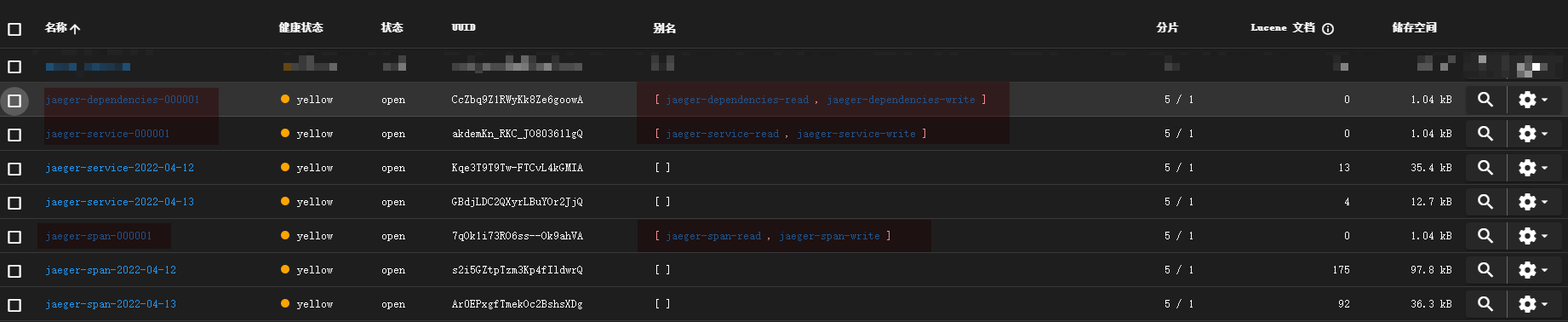
注意图中标记的部分。
下一步修改 jaeger 的启动参数,我这里直接 kubectl edit -n jaeger deployment jaeger 编辑。
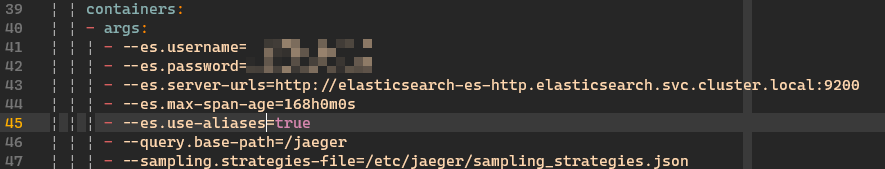
应用后自动更新 pod,注意看下日志有没有错误或者警告。对于 docker-compose 用户改法差不多,如果 jaeger 是直接 docker run 起来的,那是真的牛啤。自己 docker rm 再 docker run 一次吧。真机部署 jaeger 还没见过直接略,无非是改 systemd 配置或者 /etc/init.d 。
到这里 jaeger 部署的调整就完了,但问题还没解决:要是时间久了,会不会还创建一堆 indices?据我观察,应该不会再每天 2 个 index 的频率高强度创建 index 了(PS:因为第一天动手的时候没注意,jaeger 没加 --es.use-aliases=true,所以我也不敢说绝对不会,建议自己改了第二天看一眼。),新的 index 会写入到之前看到的 jaeger-span-000001 这种 index 里。
文档里给了个从每日创建索引转到 rollover 的迁移方法:
这不会删除旧索引,只是把旧索引合并到了别名jaeger-*-read里,让 jaeger 能查询到旧的日志。
curl -ivX POST -H "Content-Type: application/json" localhost:9200/_aliases -d '{"actions" : [{ "add" : { "index" : "jaeger-span-*-*-*", "alias" : "jaeger-span-read" } }, { "add" : { "index":"jaeger-service-*-*-*", "alias" : "jaeger-service-read" }}]}'
# archive indices
curl -ivX POST -H "Content-Type: application/json" localhost:9200/_aliases -d '{"actions" : [{ "add" : { "index" : "jaeger-span-archive", "alias" : "jaeger-span-archive-read" } }]}'
注意如果有归档的话用 第二条 curl 的同时还要给 jaeger 加上启动参数--es.archive.use-aliases=true。
轮转
到这里,问题解决了90%,但还有个问题:如果所有 jaeger 数据都放在一个 index 里,过上一段时间,数据量膨胀后会不会产生性能问题?这是很自然的想法,日志这种东西是很容易膨胀的,随时间流逝很可能堆成一座难以清理的大山:就像是你想在MySQL里往一个记录超亿级的表里插数据或删数据一样。
jaeger-es-rollover 真正的用途就是这个:轮转日志。一个 index 已经有 100M 了,那就换一个 index 吧。
# 按 CONDITIONS 指定的规则轮转
docker run -it --rm --net=host -e CONDITIONS='{"max_age": "1s"}' jaegertracing/jaeger-es-rollover:latest rollover http://localhost:9200
Rollover lets you configure when to roll over to a new index based on one or more of the following criteria:
max_age- the maximum age of the index. It uses time units:d,h,m.max_docs- the maximum documents in the index.max_size- the maximum estimated size of primary shards (since Elasticsearch 6.x). It uses byte size unitstb,gb,mb.
目前支持的条件就只有这些。rollover 并不能让 es 替你 轮转索引,所以这个 rollover 命令只能自己定时执行。
对于 docker-compose 用户或者 docker 用户我没啥好办法,也许你可以在宿主机里写一个 crontab 跑上面的docker run。
对于我这样的 kubernetes 用户则可以选择用 kubernetes 的 cronjob 实现。
apiVersion: batch/v1beta1 # 对于 kubernetes v1.21.x 已经不是 beta 了,改成 batch/v1
kind: CronJob
metadata:
name: jaeger-es-index-rollover
namespace: jaeger
spec:
schedule: "0 0 * * 0"
jobTemplate:
spec:
template:
spec:
containers:
# see document https://www.jaegertracing.io/docs/1.32/deployment/#remove-old-data
- image: jaegertracing/jaeger-es-rollover:latest
name: jaeger-es-rollover
env:
- name: CONDITIONS
value: '{"max_age":"2d"}'
args:
- rollover
- --es.username=***censored***
- --es.password=***censored***
- "http://elasticsearch-es-http.elasticsearch.svc.cluster.local:9200"
resources:
requests:
cpu: 100m
memory: 100Mi
limits:
cpu: 100m
memory: 100Mi
restartPolicy: Never
好,问题解决99%了!
删除
最后就是删除不再需要的数据了,很简单啦。下面的命令中 14 表示保留最近14天的日志,同样支持 --es.username和--es.password参数。
docker run -it --rm --net=host -e ROLLOVER=true jaegertracing/jaeger-es-index-cleaner:latest 14 http://localhost:9200
注意,虽然文档说 that is also used for daily indices,但实际发现好像并不会删。
我不确定是不是 ROLLOVER 这个环境变量的影响,建议自己试试。
elasticsearch-curator
好了,奇技淫巧环节。curator 是一个 elastic 公司开源的 python 包,介绍比较皮:
Have indices in Elasticsearch? This is the tool for you!
Like a museum curator manages the exhibits and collections on display, Elasticsearch Curator helps you curate, or manage your indices.
对不起,没去过博物馆,也没做过馆长,Get 不到。
简单地说,curator 是一个 indice 管理的工具,我们用这个工具实现找到旧索引并删除。
curator 的命令行界面像这样:
Usage: curator [OPTIONS] ACTION_FILE
Curator for Elasticsearch indices.
See http://elastic.co/guide/en/elasticsearch/client/curator/current
Options:
--config PATH Path to configuration file. Default: ~/.curator/curator.yml
--dry-run Do not perform any changes.
--version Show the version and exit.
--help Show this message and exit.
关于这个工具,我们主要关注官方文档里的两个部分:configuration file 和 action file。
configuration file 保存的是关于连接 es 所需的配置如地址、用户名密码、验证方法等,以及工具本身的配置如日志。
action file 保存的是我们希望 curator 帮我们完成的操作。
action file 的格式如下:
actions:
1:
action: ACTION1
description: OPTIONAL DESCRIPTION
options:
option1: value1
...
filters:
- filtertype: *first*
filter_element1: value1
...
2:
...
其中 action 是我们希望 curator 做的事,options 和 filters 控制 action 的行为和行为的对象。action支持很多不同的操作。
好了,现在看实例。我们想删除名称符合 jaeger-span-yyyy-mm-dd 格式的 index,并且yyyy-mm-dd小于指定的日期。
actions:
1:
action: delete_indices
description: >-
delete old jaeger-span indices
options:
ignore_empty_list: True
timeout_override:
continue_if_exception: True
disable_action: False
filters:
- filtertype: pattern
kind: prefix
value: jaeger-span
exclude:
- filtertype: age
source: name
direction: older
timestring: '%Y-%m-%d'
unit: days
unit_count: 7
exclude:
动作:delete_indices;忽略空输入,即使异常也继续执行;要删除的对象以 jaeger-span 开头,并且名称包含 %Y-%m-%d 模式的日期,且早于 7 天前。
done!把上面的配置复制一份套用到 jaeger-service-yyyy-mm-dd 上,删除 jaeger-span 的任务就算配置好了。
接下来把删除工作配置成定时任务,这里还是用了 cronjob。
先把配置保存成 ConfigMap。
---
# https://kubernetes.io/docs/concepts/configuration/configmap/
kind: ConfigMap
apiVersion: v1
metadata:
name: curator-config
namespace: jaeger
data:
curator.yml: |
client:
hosts:
- ****
- ****
- ****
port: 9200
username: ***censored***
password: ***censored***
logging:
loglevel: INFO
logformat: default
action.yml: |
actions:
1:
action: delete_indices
description: >-
delete old jaeger-span indices
options:
ignore_empty_list: True
timeout_override:
continue_if_exception: True
disable_action: False
filters:
- filtertype: pattern
kind: prefix
value: jaeger-span
exclude:
- filtertype: age
source: name
direction: older
timestring: '%Y-%m-%d'
unit: days
unit_count: 7
exclude:
2:
action: delete_indices
description: >-
delete old jaeger-service indices
options:
ignore_empty_list: True
timeout_override:
continue_if_exception: True
disable_action: False
filters:
- filtertype: pattern
kind: prefix
value: jaeger-service
exclude:
- filtertype: age
source: name
direction: older
timestring: '%Y-%m-%d'
unit: days
unit_count: 7
exclude:
再编写一个 CronJob
apiVersion: batch/v1beta1
kind: CronJob
metadata:
name: jaeger-es-index-cleanup
namespace: jaeger
spec:
schedule: "0 0 * * 0"
jobTemplate:
spec:
template:
spec:
volumes:
- name: curator-config
configMap:
name: curator-config
containers:
- image: bitnami/elasticsearch-curator:5.8.4
name: elasticsearch-curator
command:
- sh
- -c
- curator --config /cfg/curator.yml /cfg/action.yml
volumeMounts:
- mountPath: /cfg
name: curator-config
resources:
requests:
cpu: 100m
memory: 100Mi
limits:
cpu: 100m
memory: 100Mi
restartPolicy: Never
这里用了 bitnami/elasticsearch-curator 镜像,如果不信任的话可以自己写个 Dockerfile 也不会很麻烦。我主要看中 bitnami 镜像大小优化还不错(98M),要是我自己随便写一个的话可能就不止这么大了。看了眼镜像的 Dockerfile 没有什么可疑的地方就直接用啦。
对于需要立刻跑一次的情况,可以把 jobTemplate 下面的内容复制出来单独写个 Job 先跑起来。
手动
手动法我说个思路。首先你得有个 kibana console 可以访问,或者能直接请求到 es 的 9200 端口。
GET /_cat/indices 拿到 indices 列表,按名字正则过滤 jaeger-(span|service)-\d{4}-\d{2}-\d{2},然后把后面的日期解析一下;或者粗暴点,直接^(2022-04-\d{2})过滤出本月(4月)以外的所有索引,拿到一个索引列表。
具体点说,像是 kibana console 拿到的是一个每行格式如 green open jaeger-span-2022-03-01 .... 这样的纯文本,你可以放到 vscode 里然后用 Filter Lines 这样的插件快速正则过滤出来,再按 alt+shift+方向键 多光标,快速编辑出一个索引名称列表。
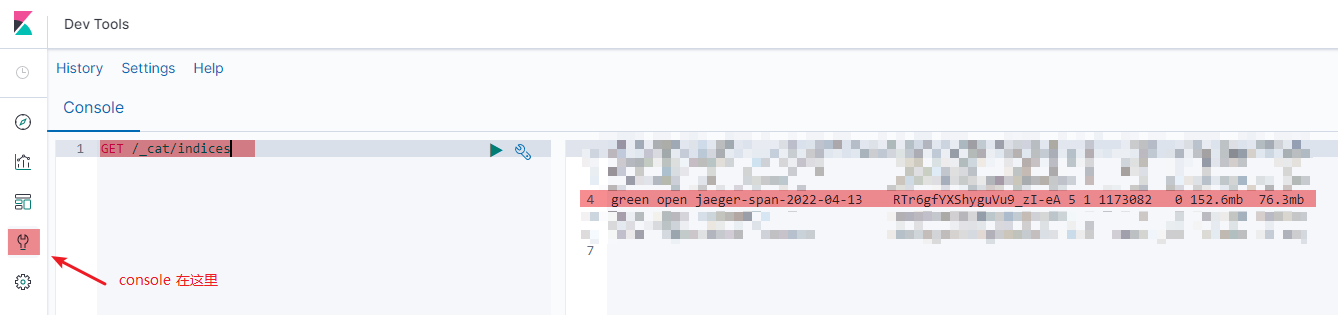
然后把索引名前面加上 DELETE /,产生 DELETE /jaeger-span-2022-03-01 这样的列表,贴到 kibana console 里,全选运行,done。
要是没 kibana ,只有 9200 访问,就改成 curl 请求,或者 httpie ,反正总有办法。最后批量执行就好。
要是都没有,讲道理啊你跟负责人说下要个访问权限好吧......
要是对自己的脚本编程能力有自信的话,大可直接写个 bash 脚本定时跑,也是 ok 的。
总结
总之,jaeger-es-rollover 配 jaeger-es-index-cleaner;或者elasticsearch-curator都行。手动法无非是手工拿到 indices 然后用各种编辑器批量编辑技巧或者正则替换,拼出个脚本。正则表达式当真是每个开发者的必备良药。
讲道理地说要不是 jaeger 给我整这一出我可能还想不到拿 es 当 jaeger 后端还会有这种坑。但这也算给我提了个醒,挂在 es 上的数据虽然不多而且都是从 MySQL 同步过去的,es 的一些基本配置如分片啥的还是得关注一下,不能只顾着接 api。这就是所谓的 运维压力 了吧。
应该还有不少小公司的开发其实是缺乏能力运维诸如 es 这样的项目的,对 MySQL 也是仅限于精通 安装和使用 ,但问起怎么怎么高可用,怎么做主备,怎么做读写分离,怎么分库分表,其实一个也不会(对,我也差不多)。
k8s 也是个很大的坑,现在甚至有点感觉后端一路走下来真正坑人的都是这些大框架,大概念,比如前段时间流行过的中台,风口上的云计算、云原生,好像沾个云就牛逼起来了。我不是说 k8s 没用嗷,我是说媒体吹的时候个个都是银弹,老板吹的时候各个都是给我也整一个!
还好压力最后都转化成了见鬼的需求和莫名其妙的技术选型,最底层的开发只要放弃思考就完事了,写什么代码不是写,大家都是给资本服务嘛。